异常的定义
在 Java 中,异常(Exception) 是程序运行过程中发生的一种错误或意外情况,可能会中断程序的正常执行流程。异常机制通过捕获和处理错误,避免程序崩溃,提供了一种高效的错误管理方式。
本质:异常是一个对象,表示程序运行中的问题。
异常的继承结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
java.lang.Object
└── java.lang.Throwable
├── java.lang.Error
│ ├── VirtualMachineError
│ │ ├── OutOfMemoryError
│ │ ├── StackOverflowError
│ │ └── InternalError
│ ├── LinkageError
│ └── AssertionError
└── java.lang.Exception
├── IOException
│ ├── FileNotFoundException
│ └── EOFException
├── RuntimeException
│ ├── NullPointerException
│ ├── ArithmeticException
│ ├── ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
│ ├── ClassCastException
│ └── IllegalArgumentException
├── SQLException
├── ParseException
└── ClassNotFoundException
|
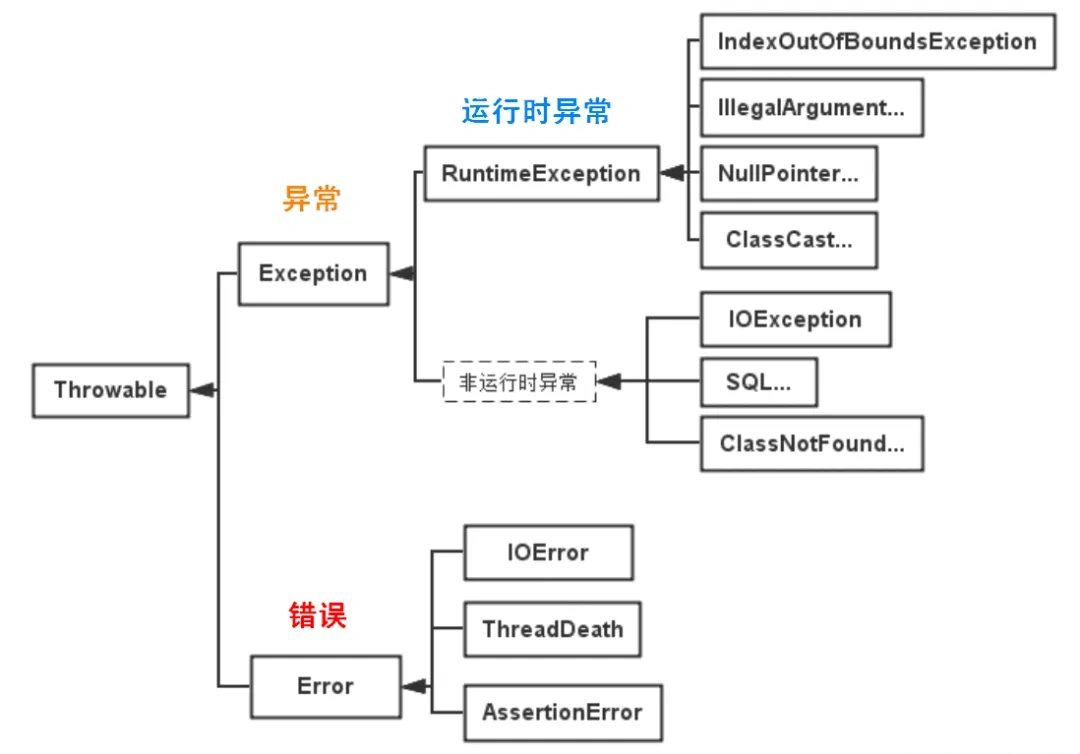
Throwable 类
- 所有错误和异常的超类。
- 定义了
printStackTrace() 、getMessage() 和 toString() 等常用方法。
Error 类
- 定义:表示程序运行时的严重问题,通常是 JVM 无法处理的情况。
- 特点
- 是
Throwable 的子类。
- 不受检查的异常,编译器不强制要求处理。
- 程序无法通过代码处理这些错误,通常由 JVM 抛出。
- 常见类型
OutOfMemoryError:JVM 堆内存耗尽。StackOverflowError:递归调用过深导致栈溢出。InternalError:JVM 内部错误。
Exception 类
定义:表示程序中可预料的问题,可以通过代码进行捕获和处理。
特点:
- 是
Throwable 的子类。
- 包括两种子类:
- 受检异常(Checked Exception):在源代码里必须显式地捕获或者抛出,否则编译器会提示你进行相应的操作。
- 非受检异常(Unchecked Exception,
RuntimeException):通常是由程序逻辑错误导致的,可以通过编码进行规避的,并不需要显式地捕获或者抛出。
Exception和Error的区别
Exception 和 Error 都是 Throwable 类的子类(在 Java 代码中只有继承了 Throwable 类的实例才可以被 throw 或者被 catch)它们表示在程序运行时发生的异常或错误情况。
总结来看:Exception 表示可以被处理的程序异常,Error 表示系统级的不可恢复错误。
-
Exception:是程序中可以处理的异常情况,表示程序逻辑或外部环境中的问题,可以通过代码进行恢复或处理。Exception 又分为 Checked Exception(编译期异常)和 Unchecked Exception(运行时异常)。
-
Error:表示严重的错误,通常是 JVM 层次内系统级的、无法预料的错误,程序无法通过代码进行处理或恢复。例如内存耗尽( OutOfMemoryError )、栈溢出( StackOverflowError )。Error 不应该被程序捕获或处理,因为一般出现这种错误时程序无法继续运行。
异常的处理方式
JVM默认处理方式
捕获并处理异常
try-catch-finally块
使用 try-catch-finally 块捕获异常并对其进行处理。
语法格式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
try {
// 可能抛出异常的代码
} catch (ExceptionType1 e1) {
// 处理 ExceptionType1 的异常
} catch (ExceptionType2 e2) {
// 处理 ExceptionType2 的异常
} finally {
// 可选:无论是否发生异常,都会执行的代码
}
|
try 块中包含可能抛出异常的代码catch 块用于捕获并处理特定类型的异常。可以有多个catch块来处理不同类型的异常。finally 块:用于定义无论是否发生异常都会执行的代码块。通常用于释放资源,确保资源的正确关闭。
执行流程
没有异常
当 try 块中没有发生异常时:
- 执行
try 块中的代码( return 之前的部分),将 return 中的返回值暂时保存。
- 跳过
catch 块。
- 执行
finally 块中的代码,如果 finally 中有 return 则覆盖之前的返回值。
return 返回值并继续执行后续代码。
try中没有return的示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.println("try block executed");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("catch block executed");
} finally {
System.out.println("finally block executed");
}
System.out.println("program continues");
}
}
// 输出:
// try block executed
// finally block executed
// program continues
|
try中有return的示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public class Main {
public static int test() {
try {
System.out.println("try block executed");
return 1; // 返回值暂时保存
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("catch block executed");
return 2;
} finally {
System.out.println("finally block executed");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Return value: " + test());
}
}
// 输出:
// try block executed
// finally block executed
// Return value: 1
|
异常发生且被捕获
当 try 块中发生异常,并且异常被 catch 块捕获时:
- 执行
try 块,直到发生异常的位置。
- 跳转到对应的
catch 块,执行 return 之前的代码,将返回值暂存。
- 执行
finally 块中的代码,如果 finally 中有 return 则覆盖之前的返回值。
- 返回之前的返回值或继续执行后续代码。
catch中没有return的示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.println("try block executed");
int result = 10 / 0; // 抛出异常
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("catch block executed: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("finally block executed");
}
System.out.println("program continues");
}
}
// 输出:
// try block executed
// catch block executed: / by zero
// finally block executed
// program continues
|
catch中有return的示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
public class Main {
public static int test() {
try {
System.out.println("try block executed");
int result = 10 / 0; // 抛出异常
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("catch block executed: " + e.getMessage());
return 2; // 被暂存
} finally {
System.out.println("finally block executed");
return 3; // 覆盖之前的返回值
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Return value: " + test());
}
}
// 输出:
// try block executed
// catch block executed: / by zero
// finally block executed
// Return value: 3
|
特点
- 当不出现异常时,
try 块中的代码正常执行
- 当
try 块中可能出现多种异常时,书写多个对应的 catch 块捕获异常
- 一个
catch 只能处理一种异常
- 可以在
catch 块中同时捕获多种异常,异常之间用|隔开,表示多种异常采用相同的处理方式
- 当
try 中的异常没有被捕获则执行JVM默认异常处理方式
- 尽量将特定的异常放在前面,通用型的异常放在后面,不然编译器只会提示通用型的异常,其他的
catch 块永远也不会执行
finally 块的特点
- 如果
finally 块中包含 return 语句,会覆盖 try 或 catch 块中的 return 值。
finally 块前面必须有 try 块,不要把 finally 块单独拉出来使用。编译器也不允许这样做。finally 块不是必选项,有 try 块的时候不一定要有 finally 块。- 如果
finally 块中的代码可能会发生异常,也应该使用 try-catch 进行包裹。
- 即便是
try 块中执行了 return 、break、continue 这些跳转语句, finally 块也会被执行。
- 如果
catch 块抛出一个异常,而 finally 块中也抛出异常,那么最终抛出的将是 finally 块中的异常。 catch 块中的异常会被丢弃,而 finally 块中的异常会覆盖并向上传递。
finally 块中的逻辑一定被执行,无论是否出现异常,如果在 try 或 catch 块中调用了 System.exit() 方法,或者程序被强制终止, finally 块不会执行
try-with-resources 块
try-with-resources 是 Java 中的一种简洁方式,用于自动管理资源。资源在使用完成后会被自动关闭,而无需显式调用 close() 方法,从而减少资源泄漏的风险。
它是在 Java 7 中引入的,资源必须实现 java.lang.AutoCloseable 接口(或其子接口 java.io.Closeable )。
语法格式
1
2
3
4
5
|
try (ResourceType resource = new ResourceType()) {
// 使用资源的代码
} catch (ExceptionType e) {
// 异常处理
}
|
ResourceType:资源类型,例如文件流、数据库连接等。
资源自动关闭:在 try 块结束后,resource 会自动调用 close() 方法。
示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MultiResourceExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("input.txt"));
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("output.txt")
) {
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
writer.write(line + "\n");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Error occurred: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
|
抛出异常
在方法声明中使用 throws 关键字
在方法体中使用 throw 手动抛出异常
throws关键字
- 作用:声明一个方法可能抛出的异常,将异常传递给调用者来处理,用于通知调用该方法的代码,必须处理这些异常。
- 语法:放在方法签名中,位于参数列表和方法体之间。
- 适用范围:主要用于受检异常(Checked Exception)。
- 支持多个异常:可以在
throws 后列出多个异常类型,用逗号分隔。
语法格式
1
|
method() throws ExceptionType { ... }
|
使用 throws 关键字,在方法签名上声明可能会抛出的异常,然后在调用该方法的地方使用 try-catch 进行处理。”
示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public static void main(String args[]){
try {
myMethod1();
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
// 算术异常
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
// 空指针异常
}
}
public static void myMethod1() throws ArithmeticException, NullPointerException{
// 方法签名上声明异常
}
|
throw 关键字
- 作用:在方法体或代码块中,实际抛出一个异常对象,用于在代码中触发异常处理逻辑
- 语法:后面必须紧跟一个异常对象的实例(
new ExceptionType(...))。
- 适用范围:可以抛出任何异常(受检异常和运行时异常)。
- 每次只能抛出一个异常:不能同时抛出多个异常。
自定义异常
在 Java 中,除了使用内置异常(如 IOException 或 NullPointerException),还可以根据具体需求定义自己的异常类。自定义异常通常用于表示应用程序中的特定错误场景,提供更清晰的错误语义。
实现方法
定义异常类:根据业务逻辑定义异常类
继承现有异常类:
- 通常从
Exception 或 RuntimeException 类派生。
- 如果希望异常必须被显式捕获(受检异常),继承
Exception 。
- 如果希望异常可以被选择性捕获(非受检异常),继承
RuntimeException 。
提供构造函数:
- 提供默认构造函数。
- 提供接受错误消息和/或原因(
Throwable)的构造函数。
定义受检异常
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
// 自定义受检异常
class CustomCheckedException extends Exception {
public CustomCheckedException() {
super();
}
public CustomCheckedException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public CustomCheckedException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public CustomCheckedException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}
public class CheckedExceptionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
throwCustomException();
} catch (CustomCheckedException e) {
System.out.println("Caught exception: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
public static void throwCustomException() throws CustomCheckedException {
throw new CustomCheckedException("This is a custom checked exception");
}
}
|
定义非受检异常
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
// 自定义非受检异常
class CustomUncheckedException extends RuntimeException {
public CustomUncheckedException() {
super();
}
public CustomUncheckedException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public CustomUncheckedException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public CustomUncheckedException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}
public class UncheckedExceptionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
throwCustomException();
} catch (CustomUncheckedException e) {
System.out.println("Caught exception: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
public static void throwCustomException() {
throw new CustomUncheckedException("This is a custom unchecked exception");
}
}
|
