MyBatis-Plus对MyBatis的改进
- 无侵入:只做增强不做改变,引入它不会对现有工程产生影响,如丝般顺滑
- 损耗小:启动即会自动注入基本 CURD,性能基本无损耗,直接面向对象操作
- 强大的 CRUD 操作:内置通用 Mapper、通用 Service,仅仅通过少量配置即可实现单表大部分 CRUD 操作,更有强大的条件构造器,满足各类使用需求
- 支持 Lambda 形式调用:通过 Lambda 表达式,方便的编写各类查询条件,无需再担心字段写错
- 支持主键自动生成:支持多达 4 种主键策略(内含分布式唯一 ID 生成器 - Sequence),可自由配置,完美解决主键问题
- 支持 ActiveRecord 模式:支持 ActiveRecord 形式调用,实体类只需继承 Model 类即可进行强大的 CRUD 操作
- 支持自定义全局通用操作:支持全局通用方法注入( Write once, use anywhere )
- 内置代码生成器:采用代码或者 Maven 插件可快速生成 Mapper 、 Model 、 Service 、 Controller 层代码,支持模板引擎,更有超多自定义配置等您来使用
- 内置分页插件:基于 MyBatis 物理分页,开发者无需关心具体操作,配置好插件之后,写分页等同于普通 List 查询
- 分页插件支持多种数据库:支持 MySQL、MariaDB、Oracle、DB2、H2、HSQL、SQLite、Postgre、SQLServer 等多种数据库
- 内置性能分析插件:可输出 SQL 语句以及其执行时间,建议开发测试时启用该功能,能快速揪出慢查询
- 内置全局拦截插件:提供全表 delete 、 update 操作智能分析阻断,也可自定义拦截规则,预防误操作
MyBatis和MyBatis-Plus开发流程的区别
MyBatis开发流程
-
引入相关依赖
-
定义被@Mapper注解修饰mapper接口以及相关方法
1 2 3 4@Mapper public interface DistrictMapper { List<District>searchAll(String tname); } -
在对应mapper.xml文件中书写对应的SQL语句或者在mapper接口中使用注解书写SQL语句
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" > <mapper namespace="org.example.operator.mapper.DistrictMapper"> <select id="searchAll" resultType="org.example.operator.pojo.entity.District"> select did,dname,tdid,content,d_url,district.tid from district left join theme on district.tid = theme.tid where theme.tname = #{tname} </select> </mapper> -
在Service层中创建对应的Service接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7package org.example.operator.service; import org.example.operator.pojo.dto.District.DistrictDTO; public interface DistrictDetailService { public void updateDistrictDetail(DistrictDTO districtDTO,String oldName); } -
以及Service接口的实现类注入Mapper对象实现业务逻辑
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47package org.example.operator.service.impl; import org.example.operator.common.exception.District.DistrictNotFound; import org.example.operator.common.exception.Theme.ThemeNotFound; import org.example.operator.common.utils.AliyunOSSUtils; import org.example.operator.mapper.DistrictMapper; import org.example.operator.mapper.ThemeMapper; import org.example.operator.pojo.dto.District.DistrictDTO; import org.example.operator.pojo.entity.District; import org.example.operator.pojo.entity.Theme; import org.example.operator.service.DistrictDetailService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; @Service public class DistrictDetailServiceImpl implements DistrictDetailService { @Autowired private ThemeMapper themeMapper; @Autowired private DistrictMapper districtMapper; @Autowired private AliyunOSSUtils aliyunOSSUtils; @Transactional @Override public void updateDistrictDetail(DistrictDTO districtDTO, String oldName) { String tname = districtDTO.getTname(); Theme theme = themeMapper.getThemeByName(tname); if (theme == null) { throw new ThemeNotFound("主题不存在"); } District district = districtMapper.getDistrictByName(oldName); if (district == null) { throw new DistrictNotFound("展品不存在"); } String durl = district.getD_url(); aliyunOSSUtils.deleteExhibitImage(durl); Long did = district.getDid(); Long tid = themeMapper.getThemeIdByName(districtDTO.getTname()); districtDTO.setDid(did); districtDTO.setTid(tid); districtMapper.updateDistrictDetail(districtDTO); districtMapper.updateDistrictTdid(districtDTO); } } -
在Controller层使用Service接口对象进行响应
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile; @RestController @Slf4j @RequestMapping("Operator/productDetail") public class DistrictDetailController { @Autowired private DistrictSummeryService districtSummeryService; @Autowired private AliyunOSSUtils aliyunOSSUtils; @Autowired private DistrictDetailService districtDetailService; @RequestMapping("/getProduct") public Result<DistrictDetailVO> getProduct(String dname) { try{ DistrictDetailVO districtDetailVO = districtSummeryService.getDistrictDetail(dname); log.info("展品详情:{}", districtDetailVO); return Result.success("查询展品详情成功",districtDetailVO); } catch (Exception e){ log.error("查询展品详情失败"); return Result.error("查询展品详情失败"); } } }
MyBatis-Plus开发流程
-
引入相关依赖
-
自定义Mapper继承MyBatis-Plus提供的接口BaseMapper,对于自定义SQL语句可以在对应mapper.xml文件中书写
1 2 3public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User>{ } -
在Service层自定义Service接口继承IService接口
1 2 3public interface IUserService extends IService<User>{ } -
自定义Service实现类,实现自定义接口并继承Servicelmpl类,注入Mapper对象实现业务逻辑(Wrapper条件构造器在这里使用)
1 2 3 4@Service public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper,User> implements IUserService{ } -
在Controller层使用Service接口对象进行响应
具体使用
-
引入依赖(参见官方文档 ),MyBatisPlus官方提供了starter,其中集成了Mybatis和MybatisPlus的所有功能,并且实现了自动装配效果。因此我们可以用MybatisPlus的starter代替Mybatis的starter:
1 2 3 4 5<dependency> <groupId>com.baomidou</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-plus-spring-boot3-starter</artifactId> <version>3.5.9</version> </dependency> -
定义Mapper:自定义Mapper继承MyBatis-Plus提供的接口BaseMapper
1 2 3public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User>{ }
默认配置
MyBatis-Plus通过扫描实体类,利用反射机制获取实体类的信息作为数据库表的信息
- 类名驼峰转下划线作为表名
- 名为id的字段作为主键
- 变量名驼峰转下划线作为表的字段名
|
|
|
|
自定义配置
如果不符合Mybatis-Plus的约定就要使用自定义配置。
基于注解的配置
- @TableName:用来指定表名(该注解用于指定实体类对应的数据库表名。当实体类名与数据库表名不一致,或者实体类名不是数据库表名的驼峰写法时,您需要使用这个注解来明确指定表名。)
- @TableId:用来指定表中的主键字段信息
- value:对应数据库表中的主键字段名
- type:主键策略
- AUTO:数据库自增长
- INPUT:通过set方法自行输入
- ASSIGN_ID:分配id
- @TableField :用来指定表中的普通字段信息
- 使用场景
- 成员变量名与数据库字段名不一致
- 成员变量名以is开头,且是布尔值(经过反射处理,它会将is去掉作为数据库字段名)
- 成员变量名与数据库关键字冲突
- 成员变量名不是数据库字段(数据库中不存在该字段)
- 使用场景
具体注解参考官方文档
基于yml的注解
在SpringBoot项目中可以通过修改application.yml来配置
|
|
具体详细配置参考官方文档
条件构造器(Wrapper)
MyBatis-Plus 提供了一套强大的条件构造器(Wrapper),用于构建复杂的数据库查询条件。(BaseMapper实现简单的单表查询)
Wrapper 类允许开发者以链式调用的方式构造查询条件,无需编写繁琐的 SQL 语句,从而提高开发效率并减少 SQL 注入的风险。
通常作为mapper方法(自定义在mapper接口或者MyBatis-Plus已经实现的)的参数在service层使用
类的继承结构
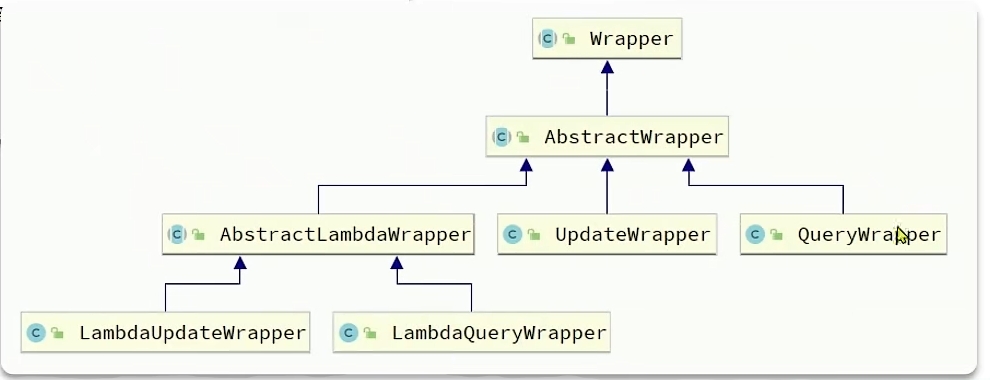
-
AbstractWrapper : 用于查询条件封装,生成 sql 的 where 条件
- QueryWrapper : Query条件封装
- UpdateWrapper : Update条件封装
- AbstractLambdaWrapper : 使用Lambda语法
- LambdaQueryWrapper :基于Lambda语法使用的查询Wrapper
- LambdaUpdateWrapper : 基于Lambda语法使用的更新Wrapper
-
QueryWrapper和LambdaQueryWrapper通常用来构建select、delete、update的where条件部分
-
UpdateWrapper和LambdaUpdateWrapper通常只有在set语句比较特殊才使用
具体使用
- 创建Wrapper对象
- Wrappers静态方法:
public static <T> QueryWrapper<T> query()
- 通过QueryWrapper对象的构造方法:
public QueryWrapper()
- 通过
lambda方法可以将普通Wrapper转换成lambdaWrapper
- Wrappers静态方法:
- 基于复杂条件构建wrapper,使用链式编程
示例方法
|
|
条件方法
| 方法名 | 解释 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| eq | 等于 = | eq(“name”, “老王”)**--->** name = ‘老王’ |
| ne | 不等于 <> | ne(“name”, “老王”)**--->** name <> ‘老王’ |
| gt | 大于 > | gt(“age”, 18)**--->** age > 18 |
| ge | 大于等于 >= | ge(“age”, 18)**--->** age >= 18 |
| lt | 小于 < | lt(“age”, 18)**--->** age < 18 |
| le | 小于等于 <= | le(“age”, 18)**--->** age <= 18 |
| between | between 值1 and 值2 | between(“age”, 18, 30)**--->** age between 18 and 30 |
| notBetween | not between 值1 and 值2 | notBetween(“age”, 18, 30)**--->** age not between 18 and 30 |
| like | LIKE ‘%值%’ | like(“name”, “王”)**--->** name like ‘%王%’ |
| notLike | NOT LIKE ‘%值%’ | notLike(“name”, “王”)**--->** name not like ‘%王%’ |
| likeLeft | LIKE ‘%值’ | likeLeft(“name”, “王”)**--->** name like ‘%王’ |
| likeRight | LIKE ‘值%’ | likeRight(“name”, “王”)**--->** name like ‘王%’ |
| isNull | 字段 IS NULL | isNull(“name”)**--->** name is null |
| isNotNull | 字段 IS NOT NULL | isNotNull(“name”)**--->** name is not null |
| in | 字段 IN (v0, v1, …) | in(“age”, 1, 2, 3)**--->** age in (1,2,3) |
| notIn | 字段 NOT IN (v0, v1, …) | notIn(“age”, 1, 2, 3)**--->** age not in (1,2,3) |
| inSql | 字段 IN ( sql语句 ) | inSql(“id”, “select id from table where id < 3”)**--->** id in (select id from table where id < 3) |
| notInSql | 字段 NOT IN ( sql语句 ) | notInSql(“id”, “select id from table where id < 3”)**--->** id not in (select id from table where id < 3) |
| groupBy | 分组:GROUP BY 字段, … | groupBy(“id”, “name”)**--->** group by id,name |
| orderByAsc | 排序:ORDER BY 字段, … ASC | orderByAsc(“id”, “name”)**--->** order by id ASC,name ASC |
| orderByDesc | 排序:ORDER BY 字段, … DESC | orderByDesc(“id”, “name”)**--->** order by id DESC,name DESC |
| orderBy | 排序:ORDER BY 字段, … | orderBy(true, true, “id”, “name”)**--->** order by id ASC,name ASC |
| having | HAVING ( sql语句 ) | 例1:having(“sum(age) > 10”)**--->** having sum(age) > 10 例2:having(“sum(age) > {0}”, 11)**--->** having sum(age) > 11 |
| func | 主要解决条件拼接 | func(i -> if(true) {i.eq(“id”, 1)} else {i.ne(“id”, 1)}) |
| or | 拼接 OR | eq(“id”,1).or().eq(“name”,“老王”)**--->** id = 1 or name = ‘老王’ |
| and | AND 嵌套 | and(i -> i.eq(“name”, “李白”).ne(“status”, “活着”))**--->** and (name = ‘李白’ and status <> ‘活着’) |
| nested | 用于多条件拼接时 | nested(i -> i.eq(“name”, “李白”).ne(“status”, “活着”))**--->** (name = ‘李白’ and status <> ‘活着’) |
| apply | 用于拼接SQL语句 | 例1:apply(“id = 1”)**--->** id = 1 例2:apply(“id = {0}”,1)**--->** *id = 1 例3:apply(“name like {0} and age > {1}”,“%J%”,18) **\*\*--->\*\* *name like ‘%J%’ and age > 18 |
| last | 无视优化规则直接拼接到 sql 的最后 | *last(“limit 1”) **\*\*--->\*\* *在SQL语句最后面拼接:limit 1 |
| exists | 拼接 EXISTS ( sql语句 ) | exists(“select id from table where age = 1”)**--->** exists (select id from table where age = 1) |
| notExists | 拼接 NOT EXISTS ( sql语句 ) | notExists(“select id from table where age = 1”)**--->** not exists (select id from table where age = 1) |
具体参见官方文档
自定义SQL
可以利用MyBatis-Plus的Wrapper来构建复杂的where条件,然后自己定义SQL语句中剩下的部分。
-
基于Wrapper定义复杂的Where条件
-
在mapper方法参数中用
@Param注解声明wrapper变量名称,名称必须为ew或者使用注解@Param(Constants.WRAPPER)明确指定参数为 Wrapper 对象。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.Wrapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.Constants; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param; public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> { @Select("SELECT * FROM user ${ew.customSqlSegment}") List<User> selectByCustomSql(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<User> wrapper); } -
自定义SQL语句,使用
${ew.customSqlSegment}来引用 Wrapper 对象生成的 SQL 片段。1 2 3QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); queryWrapper.eq("name", "张三"); List<User> userList = userMapper.selectByCustomSql(queryWrapper);
Service层接口(IService)
MyBatis提供了Service层接口IService和默认实现类ServiceImpl
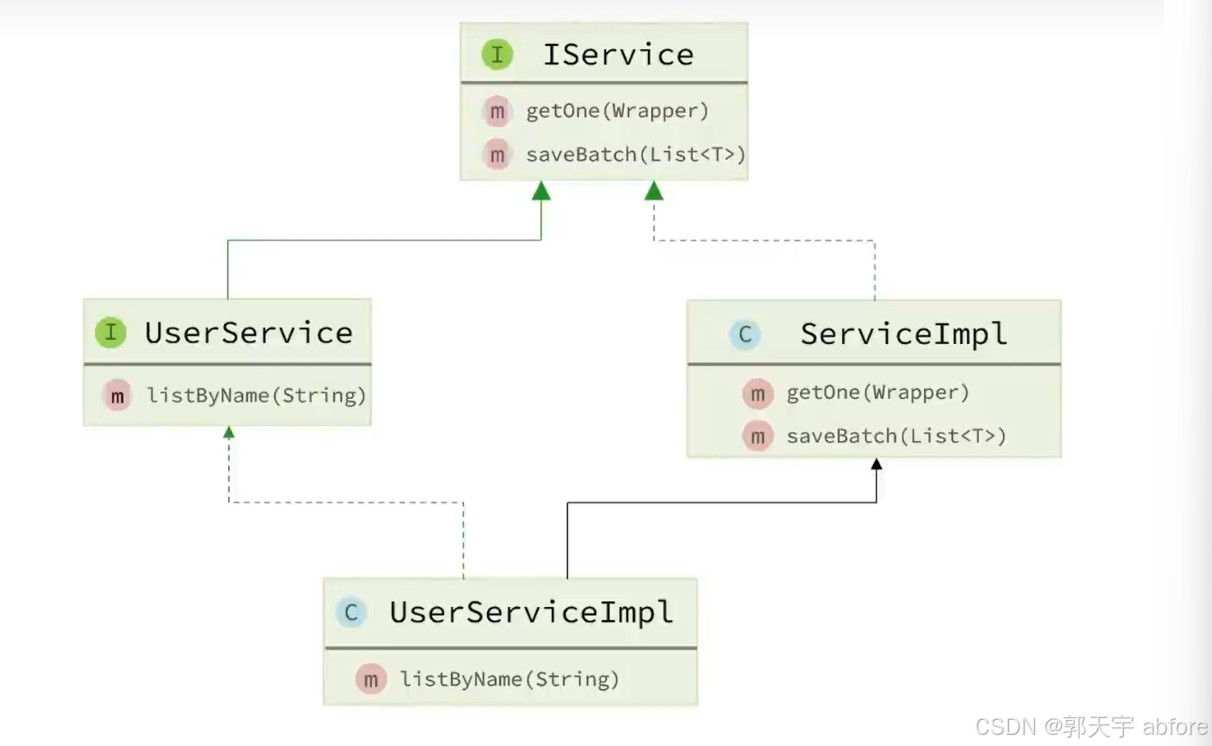
使用流程
-
自定义Service接口继承IService接口(其中IService接口中的泛型为操纵的实体类)
1 2 3public interface IUserService extends IService<User>{ } -
自定义Service实现类,实现自定义接口并继承Servicelmpl类(其中ServiceImpl中的泛型为对应的Mapper类和实体类)
1 2 3 4@Service public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper,User> implements IUserService{ }
LambdaQuery和LambdaUpdate
IService中还提供了Lambda功能来简化我们的复杂查询及更新功能。
在Service层中可以代替Wrapper实现更加复杂的查询/更新
lambdaQuery()和lambdaUpdate()方法直接获得一个Wrapper的子类通过链式编程简化
在service层中
|
|
还需要在链式编程的最后添加一个list(),这是在告诉MP我们的调用结果需要是一个list集合。这里不仅可以用list(),可选的方法有:
.one():最多1个结果.list():返回集合结果.count():返回计数结果
批量插入
|
|
效率一般:MybatisPlus的批处理是基于PrepareStatement的预编译模式,然后批量提交,最终在数据库执行时还是会有多条insert语句,逐条插入数据。而想得到最佳性能,最好是将多条SQL合并为一条。
提升效率的方式
MySQL的客户端连接参数中有这样的一个参数:rewriteBatchedStatements。顾名思义,就是重写批处理的statement语句。这个参数的默认值是false,我们需要修改连接参数,将其配置为true。
在配置文件中,在数据库连接配置中在url后面加上 rewriteBatchedStatements=true 的一个参数:
分页插件
具体参见官方文档
-
在配置类中注册MyBatis-Plus的核心插件。同时添加分页插件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24@Configuration @MapperScan("scan.your.mapper.package") public class MybatisPlusConfig { /** * 添加分页插件 */ @Bean public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() { //创建MyBatis-Plus拦截器 MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor(); //添加内部拦截器(插件) // 添加分页插件 PaginationInnerInterceptor paginationInnerInterceptor = new PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.MYSQL); //可以给分页插件添加属性 //overflow boolean false 溢出总页数后是否进行处理 //maxLimit Long 单页分页条数限制 //dbType DbType 数据库类型 //dialect IDialect 方言实现类 interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(paginationInnerInterceptor); // 如果配置多个插件, 切记分页最后添加 // 如果有多数据源可以不配具体类型, 否则都建议配上具体的 DbType return interceptor; } } -
在Mapper方法使用分页相关API
-
设置分页参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8//方法一 int pageNo = 1; //页码 int pageSize = 2; //每页大小 Page<User> pageInfo = Page.of(pageNo, pageSize); Page<User>p=userMapper.page(pageInfo); //方法二 Page<User> pageInfo = new Page<>(page,pageSize); Page<User>p = userService.page(pageInfo); -
进行分页查询
1 2Page<T> page_name=userMapper.selectPage(page, wrapper); //条件分页查询 Page<T> page_name=userMapper.page(page);//普通分页查询 -
使用相关API
1 2 3 4 5 6 7当前页数:page.getCurrent() 总页数: page.getPages() 记录数: page.getTotal() 是否有上一页: page.hasPrevious() 是否有下一页: page.hasNext() 分页数据:page.getRecords() 排序条件:page.addOrder(new OrderItem("数据库字段名",true)); //升序为true,降序为false
-